Health Insurance Meaning: An Essential Financial Safety Net
Explore the fundamentals of health insurance in our comprehensive blog, covering types of coverage, and the role of technology in the industry.
What is Health Insurance?
Health insurance is a form of insurance coverage that helps individuals and families pay for medical expenses, including routine check-ups, prescription medications, hospitalizations, surgeries, and emergency treatments. It protects policyholders from the high costs of healthcare by providing financial assistance, ensuring access to necessary medical services, and promoting overall health and well-being.
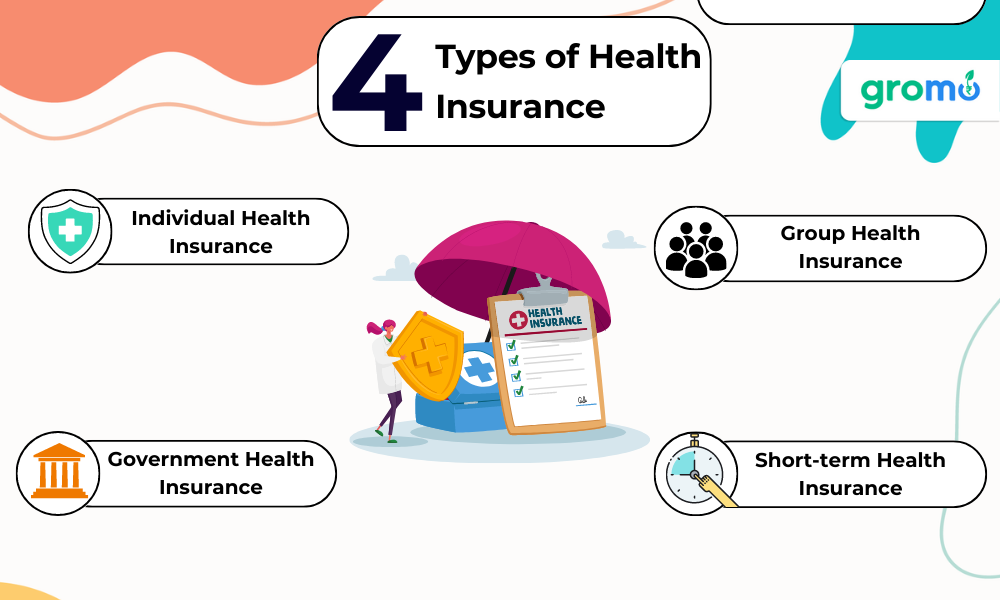
Types of Health Insurance
There are various types of health insurance plans available, each with different coverage options, payment structures, and provider networks. Some common types of health insurance include:
-
Individual Health Insurance
Individual health insurance policies are purchased by individuals to cover themselves and their dependents. These policies can be tailored to meet specific needs and may include various coverage options and deductibles. -
Group Health Insurance
Group health insurance is often provided by employers as a benefit to their employees. These plans typically cover a large group of people and offer lower premiums due to the risk being spread across a larger population. -
Government-sponsored Health Insurance
Government-sponsored health insurance programs, such as Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), provide coverage for specific populations, such as senior citizens, low-income individuals, and children. -
Short-term Health Insurance
Short-term health insurance policies offer temporary coverage for a specific period, usually between 30 days and 12 months. These plans are often used by individuals in transition, such as those between jobs or waiting for other coverage to begin.
Key Components of Health Insurance Policies
Health insurance policies typically include several key components that determine the scope and cost of coverage:
Premiums: The monthly or annual fee paid by the policyholder to maintain coverage.
Deductibles: The amount the policyholder must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in.
Copayments: A fixed amount paid by the policyholder for specific services or medications, with the insurance company covering the remaining costs.
Coinsurance: The percentage of healthcare costs shared between the policyholder and the insurance company after the deductible has been met.
Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The maximum amount the policyholder must pay out-of-pocket for covered expenses during a policy period, after which the insurance company covers 100% of the costs.
Understanding these components can help individuals make informed decisions about their health insurance coverage and budget for healthcare expenses accordingly.
ALSO CHECK OUT!!
- Demat Account Meaning: Meaning, Significance, and Other Key Details
- Savings Account Meaning: Important Related Terms
- Vehicle Loan Interest Rate: What Is The Meaning Of Vehicle Loan Interest?
- Benefits Of Health Insurance: 5 Benefits Of Health Insurance
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Premiums
Health insurance premiums can vary depending on several factors, such as:
-
Age: Older individuals typically have higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of health issues.
-
Gender: Gender can influence premiums, as women may have higher costs for services like maternity care.
-
Tobacco Use: Smokers often face higher premiums due to the increased risk of health problems related to tobacco use.
-
Geographic Location: Premiums can vary by region due to differences in healthcare costs and provider networks.
-
Plan Type: Premiums may differ based on the type of health insurance plan, such as individual or group coverage, and the specific features of the plan.
By considering these factors, individuals can better understand the costs associated with health insurance and make informed decisions about their coverage options.
The Importance of Health Insurance in Financial Planning
Health insurance plays a crucial role in financial planning by providing a safety net against unexpected medical expenses, which can otherwise lead to significant financial strain or even bankruptcy.
The benefits of health insurance in financial planning include:
Protection Against High Medical Costs: Health insurance helps policyholders manage the financial risks associated with healthcare, ensuring they have access to necessary medical services without facing prohibitive costs.
Improved Access to Care: Health insurance increases access to a wide range of healthcare providers and services, ensuring that policyholders receive timely and appropriate care when needed, which can contribute to better overall health outcomes.
Preventive Care: Many health insurance plans cover preventive care services, such as vaccinations and routine screenings, at no cost to the policyholder. This encourages individuals to maintain their health and catch potential issues early, reducing the likelihood of more serious and costly health problems later on.
Budgeting for Healthcare Expenses: Health insurance allows individuals to better budget for healthcare costs by spreading expenses over time through regular premium payments, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums. This can provide greater financial stability and predictability for policyholders.
Financial Peace of Mind: Knowing that they have financial protection in the event of a medical emergency can provide policyholders with peace of mind, allowing them to focus on their health and well-being without the added stress of potential financial hardship.
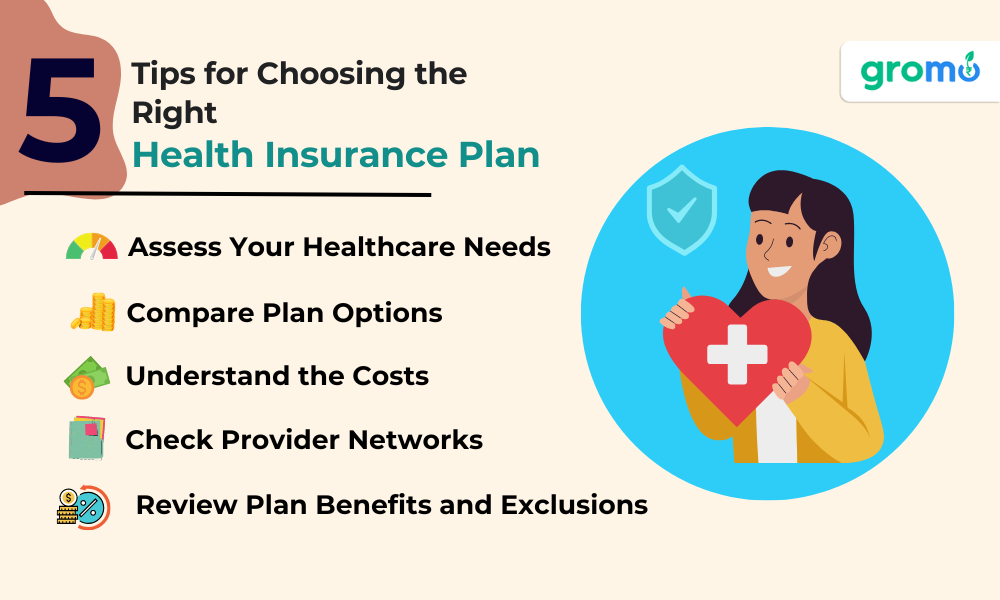
Tips for Choosing the Right Health Insurance Plan
When selecting a health insurance plan, consider the following tips to ensure you find the best coverage for your needs and budget:
-
Assess Your Healthcare Needs: Consider your current and future healthcare needs, including any ongoing medical conditions, prescription medications, and anticipated life changes, such as starting a family or retiring.
-
Compare Plan Options: Research and compare various health insurance plans, taking into account factors such as coverage, provider networks, deductibles, copayments, coinsurance, and out-of-pocket maximums.
-
Understand the Costs: Be aware of the total costs associated with a health insurance plan, including premiums, deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. This will help you make an informed decision based on your financial situation and healthcare needs.
-
Check Provider Networks: Ensure that your preferred healthcare providers and facilities are included in the plan's network, as out-of-network services can result in higher out-of-pocket costs.
-
Review Plan Benefits and Exclusions: Carefully review the benefits and exclusions of each plan to ensure it provides adequate coverage for your healthcare needs and avoids any unpleasant surprises.
DOWNLOAD GROMO!!
and sell as many financial products as you want, gain knowledge about these products and earn much more with each sale!
Health Insurance and the Role of Government
Governments play a critical role in the provision and regulation of health insurance, ensuring that individuals have access to affordable and high-quality healthcare services.
Some of the ways governments contribute to the health insurance landscape include:
1. Public Health Insurance Programs
Governments often establish public health insurance programs to provide coverage for specific populations, such as the elderly, low-income individuals, and children. Examples of these programs in the United States include Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP).
2. Healthcare Legislation and Regulation
Governments regulate the health insurance industry to protect consumers and promote access to affordable care. This can include setting minimum coverage standards, enforcing consumer protections, and overseeing the financial solvency of insurance companies.
3. Subsidies and Tax Credits
To make health insurance more affordable, governments may provide subsidies or tax credits to individuals and families based on income or other qualifying factors. These financial incentives can help lower the cost of premiums, making health insurance more accessible to those who might otherwise be unable to afford coverage.
4. Health Insurance Exchanges
In some countries, governments establish health insurance exchanges or marketplaces to facilitate the comparison and purchase of health insurance plans. These platforms provide a centralized location where consumers can compare plan options, review pricing, and enroll in coverage.
5. Public Health Initiatives
Governments invest in public health initiatives aimed at improving overall health and well-being, which can have a positive impact on health insurance costs. These initiatives may include promoting preventive care, funding research, and supporting community health programs.
The Impact of Health Insurance on Society
Health insurance has wide-ranging effects on society, influencing both individual health outcomes and broader economic and social factors. Some of the key impacts of health insurance on society include:
Improved Health Outcomes: Health insurance promotes access to necessary medical care, resulting in better overall health outcomes and increased life expectancy for those with coverage.
Reduced Healthcare Disparities: Access to health insurance can help reduce disparities in healthcare utilization and outcomes among different socioeconomic and demographic groups, promoting health equity across society.
Economic Benefits: Health insurance supports economic stability by reducing the financial burden of healthcare costs on individuals, families, and businesses, while also driving demand for healthcare services and supporting job creation within the healthcare sector.
Workforce Productivity: Healthier individuals are more likely to be productive members of the workforce, contributing to economic growth and overall societal well-being.
Social Safety Net: Health insurance serves as a critical component of the social safety net, providing financial protection and access to care for those who might otherwise face significant hardship due to illness or injury.
Recognizing the far-reaching effects of health insurance on society, it is important for governments, healthcare providers, and individuals to work together to ensure that everyone has access to the care and coverage they need to lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
Employer-sponsored Health Insurance
Many employers offer health insurance benefits to their employees as part of their overall compensation package. This is known as employer-sponsored health insurance. Here are some key features and benefits of employer-sponsored health insurance:
1. Group Coverage
Employer-sponsored health insurance typically provides coverage for a large group of employees, which allows the insurer to spread risk across a larger population, often resulting in lower premiums for individual employees compared to individual health insurance plans.
2. Cost Sharing
In most cases, employers and employees share the cost of health insurance premiums. This means that the employer pays a portion of the premium, and the employee contributes the remaining amount, usually through payroll deductions. This cost-sharing arrangement can make health insurance more affordable for employees.
3. Tax Benefits
Employer-sponsored health insurance premiums are typically paid on a pre-tax basis, meaning that the amount is deducted from an employee's salary before taxes are calculated. This can result in tax savings for the employee, as they are effectively paying for their health insurance with pre-tax dollars.
4. Access to a Wide Range of Plans
Employers often offer their employees a choice of health insurance plans, allowing employees to select the plan that best meets their needs and budget. This can include options for different provider networks, coverage levels, and cost-sharing arrangements.
5. Family Coverage
Employer-sponsored health insurance plans often extend coverage to an employee's spouse and dependents, ensuring that the entire family has access to affordable healthcare.
ALSO CHECK OUT!
- How To Improve CIBIL Score Using Your Credit Card?
- How To Apply For A Home Loan With Low CIBIL Score?
- Investment Products: What Are Investment Products?
- Demat Account Meaning: Meaning, Significance, and Other Key Details
The Role of Technology in Health Insurance
As technology continues to advance, it is increasingly impacting the health insurance industry, offering new opportunities for innovation, cost savings, and improved consumer experiences. Some ways technology is transforming health insurance include:
-
Telemedicine: The use of telemedicine and virtual healthcare services has expanded rapidly in recent years, offering patients more convenient access to healthcare providers while also reducing healthcare costs. Many health insurance plans now cover telemedicine services, which can help to further increase their adoption.
-
Wearables and Health Data: Wearable devices and other health monitoring tools can collect valuable data on an individual's health habits and status. This data can be used by health insurance companies to better assess risk, tailor coverage, and offer incentives for healthy behaviors.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI technologies are being applied to various aspects of the health insurance industry, including underwriting, claims processing, and customer service. This can lead to increased efficiency, cost savings, and improved consumer experiences.
-
Personalized Medicine: Advances in personalized medicine, such as genomics and precision medicine, can help healthcare providers deliver more targeted and effective treatments. This has the potential to improve health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs, ultimately benefiting both patients and health insurance companies.
-
Online Platforms and Tools: Technology has enabled the development of online platforms and tools that make it easier for consumers to compare health insurance plans, enroll in coverage, and manage their policies. These platforms can improve transparency, increase consumer choice, and drive competition within the health insurance market.
Embracing technology and innovation in the health insurance industry can lead to improved access to care, better health outcomes, and more affordable coverage options for consumers.
Health insurance plays a critical role in individual financial planning, societal well-being, and overall public health. By understanding the various types of health insurance, the role of employers and government, and the impact of technology on the industry, individuals and policymakers can work together to create a healthcare system that meets the needs of all citizens, promoting a healthier and more equitable society.
Sell financial products online, and earn a substantial income with gromo app!
KEY TAKEWAYS
-
Health insurance provides financial protection and access to healthcare, promoting overall health and well-being.
-
Understanding policy components, such as premiums, deductibles, and copayments, is crucial for making informed decisions about coverage.
-
Governments play a key role in health insurance through public programs, regulation, and subsidies.
-
Employer-sponsored health insurance offers group coverage, cost-sharing, and tax benefits for employees.
-
Technological advancements are transforming the health insurance industry, with innovations like telemedicine, wearables, and AI driving improvements in care and affordability.









